Qaiwan International University’s participation at the third at Erbil International Fair
QIU,Erbil International Fair
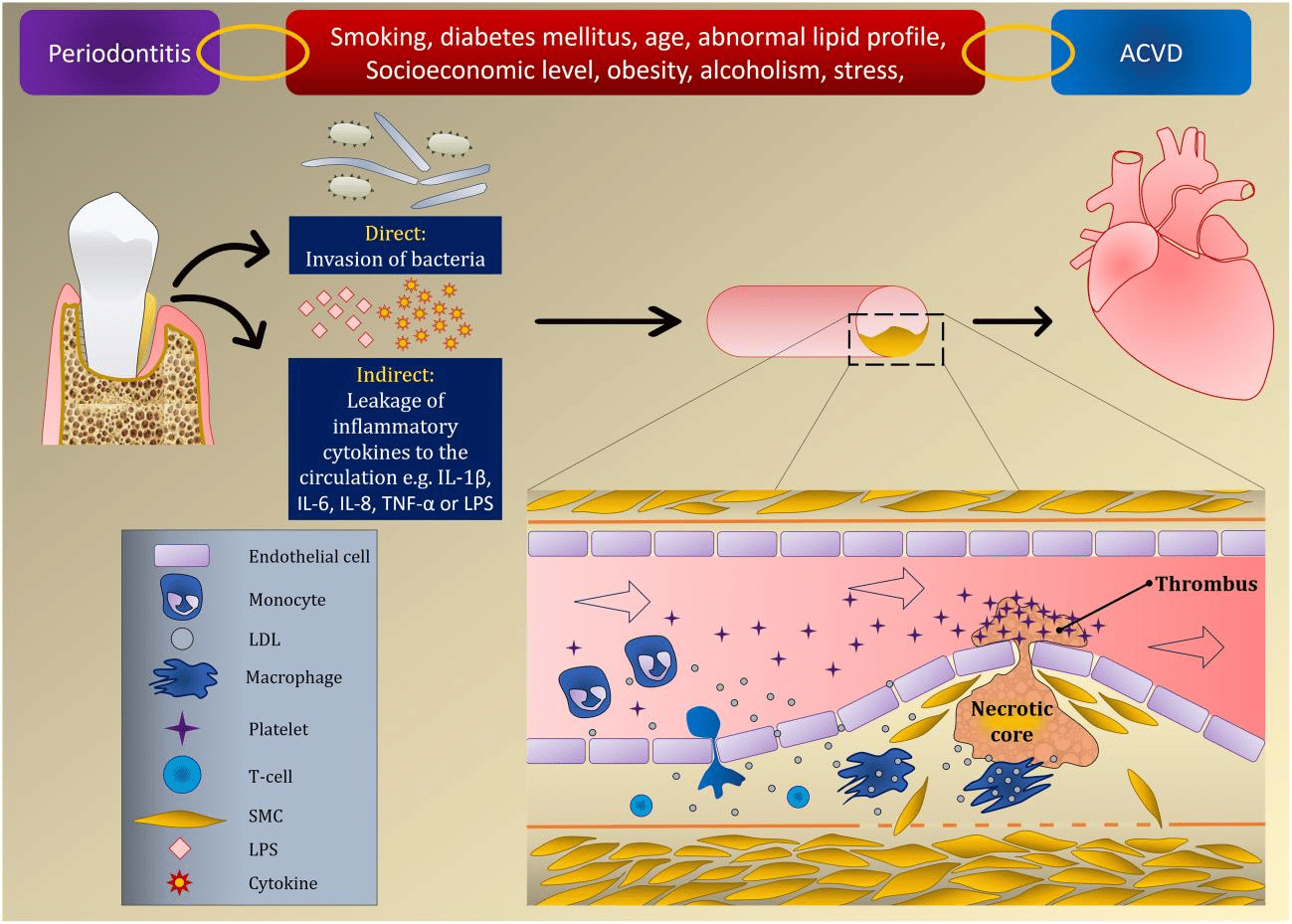
The old saying "healthy mouth, healthy body" isn't just a catchy phrase; it's backed by scientific evidence that highlights the intricate relationship between oral health and overall well-being. Among the various oral health concerns, periodontitis stands out not only for its impact on oral health but also for its potential to influence systemic conditions throughout the body.
Periodontitis, commonly known as gum disease, is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It typically begins with gingivitis, characterized by swollen
and bleeding gums, and if left untreated, progresses to periodontitis, leading to gum recession, bone loss, and ultimately tooth loss.
However, what many may not realize is that periodontitis is not confined to the oral cavity; it can also have far-reaching effects on systemic health. Research has revealed compelling links between
periodontitis and several systemic conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, respiratory diseases, and even certain cancers.
The association between periodontitis and cardiovascular diseases, such as heart disease and stroke, has been extensively studied. The inflammatory response triggered by periodontal bacteria can contribute to the development and progression of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), potentially increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Similarly, the relationship between periodontitis and diabetes is bidirectional. Poorly controlled diabetes can impair the body's ability to fight infections, including those in the gums, making individuals with
diabetes more susceptible to periodontal disease. Conversely, periodontitis can exacerbate diabetes by causing insulin resistance and difficulty in controlling blood sugar levels.
Respiratory diseases, including pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), have also been linked to periodontitis. The inhalation of oral bacteria from infected gums can potentially reach the lungs and contribute to respiratory infections, particularly in individuals with compromised immune systems.
Furthermore, emerging research suggests associations between periodontitis and conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, Alzheimer's disease, and certain cancers, though the exact mechanisms remain
under investigation. Understanding the interplay between periodontitis and systemic conditions underscores the importance of holistic approaches to healthcare. Dentists and physicians alike recognize the significance of comprehensive patient care, where oral health is considered an integral component of overall health.

Preventive measures, including regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene practices, and lifestyle modifications, play a crucial role in managing both periodontal disease and its potential systemic
consequences. Early detection and treatment of periodontitis not only preserve oral health but may also contribute to reducing the risk of associated systemic conditions.
In conclusion, the link between periodontitis and systemic conditions serves as a poignant reminder of the interconnection of the human body. By prioritizing oral health and recognizing its implications
for systemic well-being, we can strive towards a healthier future, one smile at a time.
|
Professor Faraedon M. Mostafa Zardawi currently is the Dean of the Faculty of Dentistry at Qaiwan International University. Professor Faraedon teaches undergraduate students two courses; patient care, professionalism, comprehensive care and practice management. He does research in Dentistry, soft tissue facial prosthesis, and Periodontics. At University of Sulaimani, he teaches post graduate students of Periodontics. He has more than 75 published articles, one book and four chapters published in Ebooks. Email: Faraedon.mostafa@uniq.edu.iq |
QIU © All Rights Reserved | by QIU IT-Office | @ 2022 QIU University